

More than 200 Distributors
Around 1,000,000 Outlets
Nationwide Coverage
Qumic
(Levofloxacin)
Brand Name
Qumic
Generic Name
(Levofloxacin)
Therapeutic Segment
Antibiotic (Quinolone)

Scan QR code to open on your mobile device.
Available as
- DROPS
- QUMIC EYE DROPS
- INFUSION
- QUMIC 500MG/100ML INFUSION
- TABLET
- QUMIC 250MG TABLET
- QUMIC 500MG TABLET
- QUMIC 750MG TABLET
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
COMPOSITION
Qumic 250 mg Tablets
Each film-coated tablet of Qumic 250mg contains 250mg of levofloxacin as active ingredient. corresponding to 255mg of Levofloxacin Hemihydrate.
Qumic 500 mg Tablet
Each film-coated tablet of Qumic 500mg contains 500mg of levofloxacin as active ingredient. corresponding to 512.46 mg of Levofloxacin Hemihydrate.
Qumic 750 mg Tablet
Each film-coated tablet of Qumic 750mg contains 750mg of levofloxacin as active ingredient. corresponding to 765mg of Levofloxacin Hemihydrate.
Qumic 500 I.V Infusion
Each vial of 100 ml contains 500mg of Levofloxacin. corresponding to 512.46 mg of Levofloxacin Hemihydrate.
Qumic 750 I.V Infusion
Each vial of 150 ml contains 750mg of Levofloxacin. corresponding to 765mg of Levofloxacin Hemihydrate.
PHYSICOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF THE ACTIVE INGREDIENT:
Nonproprietary name: Levofloxacin
Abbreviation: LVFX
Chemical name: (–)-(S)-9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7H- pyrido [1,2,3-de][1,4] benzoxazine 6 –carboxylic acid hemihydrate Structural formula:
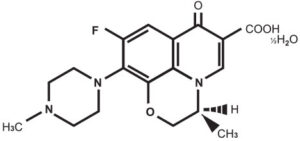
Molecular formula: C18H20FN3O4 ½H2O
Molecular weight: 370.38
Melting point: 222-2300C (decomposition)
Description: Light yellowish white to yellowish.
White crystals or crystalline powder, odorless and bitter taste. Freely soluble in glacial acetic acid and methanol, sparingly soluble in ethanol, and practically insoluble in ether. Light sensitive.
PHARMACOLOGY:
Antibacterial Activity
Qumic is a wide-spectrum antibacterial agent against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including anaerobes. Qumic has shown strong antibacterial activities against Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes/ Streptococcus hemolyticus, Enterobacter spp., Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp., Serratia spp., Enterococcus spp., Proteus spp., and other glucose non-fermentative gram-negative rods, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Moreover, Qumic has shown antibacterial activity against Chlamydia trachomatis.
MECHANISM OF ACTION:
The main mechanism of action of Qumic is the inhibition of DNA gyrase. It is twofold stronger than that of ofloxacin. here is not much difference between the MIC and MBC. The activity of Qumic is bactericidal. In the observation of bacterial morphology, bacteriolysis can be seen in the concentration around MIC.
PHARMACOKINETICS:
Absorption: Orally administered levofloxacin is rapidly and almost completely absorbed with peak plasma concentrations being obtained within 1hr. The absolute bioavailability is approximately 100%. Food has little effect on the absorption of levofloxacin.
Distribution In Plasma: Approximately 30-40 % of levofloxacin is bound to serum protein. 500mg once daily multiple dosing with levofloxacin showed negligible accumulation. There is modest but predictable accumulation of levofloxacin after doses of 500 mg twice daily. Steady state is achieved within 3 days.
Penetration into tissues and body fluids: Penetration into Bronchial mucosa. Epithelial Lining Fluid (ELF). Maximum levofloxacin concentrations in bronchial mucosa and epithelial lining fluid were 8.3 μg/ml and 10.8 μg/ml respectively. These were reached approximately one hour after administration.
Penetration into Lung Tissue: Maximum levofloxacin concentrations in lung tissue were approximately 11.3 μg/ml and were reached between 4 to 6 hours after administration. The concentrations in the lungs consistently exceeded those in plasma.
Penetration into Lung Tissue: Maximum levofloxacin concentrations in lung tissue were approximately 11.3 μg/ml and were reached between 4 to 6 hours after administration. The concentrations in the lungs consistently exceeded those in plasma.
Penetration into Blister Fluid: Maximum levofloxacin concentrations of about 4.0 and 6.7 μg/ml in the blister fluid were reached 2-4 hours after administration following the 1 x 500 and 2 x 500 mg doses, respectively.
Metabolism: Levofloxacin is metabolised to a very small extent, the metabolites being desmethyl-levofloxacin and levofloxacin N-oxide. These metabolites account for < 5 % of the dose excreted in urine. Levofloxacin is stereochemically stable and does not undergo chiral inversion.
Elimination: Following oral and intravenous administration, levofloxacin is eliminated relatively slowly from the plasma (t ½: 6-8 h). Excretion is primarily by the renal route (> 85 % of the administered dose.) There is no major difference in the pharmacokinetics of levofloxacin following intravenous and oral administration, suggesting that the oral and intravenous routes are interchangeable.
Subject with renal insufficiency: The pharmacokinetics of levofloxacin are affected by renal impairment. With decreasing renal function renal elimination and clearance are decreased, and elimination half-lives increased as shown in the table below.
|
Clcr (ml/min) |
< 20 |
20-40 |
50-80 |
|
ClR (ml/min) |
13 |
26 |
57 |
|
t (h) |
35 |
27 |
9 |
Elderly subjects: There are no significant differences in levofloxacin kinetics between young and elderly subjects, except those associated with difference in clearance.
General differences: Separate analysis for male and female subjects did not show clinical relevant gender differences in levofloxacin pharmacokinetics.
Non-Clinical Studies: Absorption and Distribution; 14C-levofloxacin, when administered orally to rats at a dose of 20 mg/kg, was absorbed primarily from the small intestine, and the maximum serum concentration (2.5 μg/ml) was reached 0.5 hours after administration, except for the level in the central nervous system. Levofloxacin concentration in almost all tissues of the body were higher than the serum level, demonstrating the good transference to tissues. Drug concentrations in the main organs i.e in the kidneys and liver were high and lowest in the brain.
Acute Toxicity: LD50 values after oral administration were 1881 mg/kg for mice, 1478 mg/kg for rats and more than 250 mg/kg for cynomolgus monkeys.
Subacute Toxicity: Following 4-weeks oral administration to rats, no toxicological changes in clinical signs, hematology, blood chemistry urinalysis and histopathology were observed in the 50 mg/kg and 200 mg/kg administered groups. At a dose of 800 mg/kg, however, increased M/E ratio of bone marrow
cells, decreased neutrophil count and slight degeneration of the articular cartilage of limb joint were observed. Following 4 weeks oral administration to cynomolgus monkeys, no toxicological changes were observed at doses of 10 and 30 mg/kg, but salivation, diarrhea, slight inhibition of body weight gain and decrease in urine pH were observed at 100 mg/kg.
Chronic Toxicity: Following 26 weeks oral administration to rats, no toxicological changes were observed at a dose of 20 mg/kg, but salivation and high urinary pH were observed at doses of 80 and 320 mg/kg. In addition, at a dose of 320 mg/kg, increased feces and enlargement of goblet cells in cecal mucosa were seen. Following 26 weeks oral administration to cynomolgus monkeys, no toxicological changes were observed at doses of 10.25 and 62.5 mg/kg.
Reproduction studies
(1) Fertility study: No effects were observed on fertility in either sex or on fetuses after oral administration to rats at upto 360 mg/kg.
(2) Teratogenic study: No effects were observed on fetuses or neonates after oral administration to rats upto 90 mg/kg. Moreover, lethal effects to embryos and fetuses, growth retardation in fetuses and neonates or teratogenesis were not observed in rabbits after oral administration at 50 mg/kg.
(3) Perinatal and postnatal study: No effect was observed on maternal parturition and nursing or on neonates in rats after oral administration of upto 360 mg/kg.
Antigenicity: No specific antibody to levofloxacin was produced in mice, guinea pigs, and rabbits concurrently treated with adjuvants. In PCA test using serum of experimentally sensitized animals, mice showed positive reaction, but guinea pigs and rabbits were negative and systemic anaphylactic reactions were not observed in guinea pigs.
Mutagenicity: Chromosomal aberration test and sister chromatid exchange test using cultured Chinese hamster cell showed positive results. However, in vivo studies for the same items, mouse bone marrow micronucleus test and sister chromatid exchange test results were negative. Moreover, the reverse mutation test, induced mutation frequency test, HGPRT test, in vivo unscheduled DNA synthesis test, and dominant lethal test were negative.
Effect on Kidney: Following oral administration of upto 120 mg/kg to rabbits for 10 days, no abnormalities were observed in renal function and morphology.
Effect on eyes: Eye toxicity tests in pigmented rats orally administered 100 mg/kg/day for 14 days showed no changes in electroretinogram, ophthalmological examination and histopathology.
Effect on articular cartilage: When levofloxacin was orally administered to juvenile rats (3 to 4 weeks of age) and beagle dogs (4 months) for 7 days, lesions were seen in the articular cartilage in rats at 300 mg/kg or more and in dogs at 10 mg/kg or more. Juvenile dogs were more susceptible to the chondrotoxicity. When Levofloxacin was orally administered to young adult dogs (13 months of age) for 7 days, very mild toxicity was observed at 40 mg/kg. However, in adult dogs aged 18 months in which the drug was administered for 14 days, no toxicity was observed at a high dose of 30 mg/kg.
Phototoxicity test: Albino mice were orally given levofloxacin and subsequently irradiated with UVA (wave length 320-400 nm), and auricular thickness was measured. Phototoxicity (increase in thickness) was not shown at 200 mg/kg.
Indications: The following infections caused by Staphylococcus spp.Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus hemolyticus, Enterococcus spp. Peptostreptococcus spp, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Branhamella catarrhalis, Propionibacterium acnes, Escherichia coli, Citrobacter spp. Salmonella spp. Shigella spp.Klebsiella spp, Enterobacter spp, Serratia spp, Proteus spp, vibrio cholerae, Pseudomonas aerugionosa, Haemophilus influenzae, Acinetobacter spp, Campylobacter spp. Chlamydia spp,Mycoplasma spp, Legionella spp, are susceptible to levofloxacin. Pneumonia, chronic bronchitis, diffuse panbronchiolitis, bronchiectasis with infection, secondary infections in chronic respiratory disease.
- Laryngopharyngitis, tonsillitis (peritonsillitis, peritonsillar abscess), acute bronchitis.
- Pyelonephritis, cystitis, prostatitis, epididymitis, gonococcal urethritis, non–gonococcal urethritis.
- Intrauterine infections, cervicitis, uterine adnexitis, bartholinitis.
- Folliculitis (including acne pustulosa), furuncle, furunculosis, carbuncle, impetigo contagiosa,hydradenitis, acne conglabata, infectious atheroma, periproctic abscess.
- Mastitis, (superficial) secondary infections in traumatic wounds, burns, operative wounds, etc.
- Cholecystitis, cholangitis.
- Otitis externa, otitis media, sinusitis, suppurative sialadenitis.
- Blepharitis, hordeolum, dacryocystitis, conjuctivitis, tarsadenitis, Bacterial dysentery, infectious enteritis, Salmonella enteritis, cholera.
- Peridontitis, pericoronitis, gnathitis.
POSOLOGY AND METHOD OF ADMINISTRATION:
Levofloxacin tablets are administered once or twice daily. The dosage depends on the type and severity of the infection and the sensitivity of the presumed causative pathogen. The usual dose of Qumic infusion is 500mg administered by slow infusion over 60 minutes every 24 hours or as prescribed in the dosing chart.
Duration of treatment:
The duration of therapy varies according to the course of the disease. As with antibiotic therapy in general, administration of Qumic tablets should be continued for a minimum of 48 to 72 hours after the patient has become afebrile or evidence of bacterial eradication has been obtained.
Method of administration: Qumic tablet should be swallowed with crushing and with sufficient amount of liquid. The tablets may be taken during meals or between meals. Qumic tablet should be taken two hours before iron salts, antacids and sucralfate administration since reduction of absorption can occur. Qumic Infusion should only be administered intra-venously. It is not for intramuscular, intrathecal, intraperitoneal or subcutaneous administration. Infusion should be infused intravenously slowly over a period of not less than 60 minutes. Since only limited data are available on the compatibility of Levofloxacin intravenous injection with other intravenous substance, additives or other medication should not be added to Qumic infusion or infused simultaneously through the same intra-venous line. If the same intravenous line is used for sequentional infusion of several different drugs the line should be flushed before and after infusion of Levofloxacin with an infusion solution ompatible with Levofloxacin and with any other drug administered through this common line.
The following dose recommendations can be given for Qumic:
Dosage in patients with normal renal function (creatinine clearance > 50 ml/min)
|
INDICATIONS |
TABLETS |
INFUSION |
||
|
Daily Dose (mg) |
Duration (Days) |
Daily Dose (mg) |
Duration (Days) |
|
|
Acute Bacterial Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis |
250 mg BID |
7 |
||
|
500 mg OD |
7 |
500mg OD |
7 |
|
|
Community Acquired Pneumonia |
250 mg BID |
7-14 |
||
|
500 mg OD |
7-14 |
500mg OD |
7-14 |
|
|
750 mg OD |
5 |
750mg OD |
5 |
|
|
Nosocomial Pneumonia |
750 mg OD |
7-14 |
750mg OD |
7-14 |
|
Acute Maxillary Sinusitis |
250 mg BID |
10-14 |
10-14 |
|
|
500 mg OD |
10-14 |
500mg OD |
10-14 |
|
|
750 mg OD |
5 |
750mg OD |
5 |
|
|
Complicated Urinary Tract Infections |
250 mg OD |
10 |
250mg OD |
10 |
|
750 mg OD |
5 |
750mg OD |
5 |
|
|
Acute Pyelonephritis |
250 mg OD |
10 |
250mg OD |
10 |
|
750 mg OD |
5 |
750mg OD |
5 |
|
|
Chronic bacterial prostatitis |
500 mg OD |
28 |
500mg OD |
28 |
|
Uncomplicated Skin and Soft Tissue Infection |
250 mg BID |
7-10 |
||
|
500 mg OD |
7-10 |
500mg OD |
7-10 |
|
|
Complicated Skin and Soft Tissue Infection |
750 mg OD |
7-14 |
750mg OD |
7-14 |
Note: Dosage may be adjusted according to the kind of infection and severity of the symptoms.
Dosage in patient with Impaired renal function
(Creatinine clearance < 50 ml/mm)
|
Creatinine Clearance |
Dose regimen |
||
|
mg/24h |
1 x250 mg /24 h |
1×500 mg/24 h |
1×750/24 h |
|
First dose/ always |
250 mg |
500 mg |
750 mg |
|
50-20 ml/min |
then 125 mg/24 h |
then 250 mg/24 h |
then 750mg/48 h |
|
19-10 ml/min |
then 125 mg/48 h |
then 125 mg/24 h |
then 500mg/48 h |
|
<10 ml/min |
then 125 mg/48 h |
then 125 mg/24 h |
then 500mg/48 h |
(including hemodialysis and CAPD)1
No additional doses are required after hemodialysis or continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD)
Compatible Intravenous Solution:
- 9 % Sodium Chloride Injection USP
- Plasma Lyte 56/5 % Dextrose Injection
- 5 % Dextrose Injection USP
- 5 % Dextrose, 0.45 % Sodium Chloride and 0.15 % Potassium Chloride Injection
- 5 % Dextrose / 0.9 % NaCl Injection Sodium Lactate Injection (M/6)
- 5 % Dextrose in Lactated Ringers
Dosage in elderly
No adjustment of dosage is required in the elderly, other than imposed by consideration of renal function.
PRECAUTIONS
To prevent the development of resistance, susceptibility to the drug should be determined before use. The duration of use should be limited to the minimal time required for treatment.
- Contraindications
- Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any ingredients in this product or to ofloxacin.
- Pregnant woman or women suspected of being pregnant. ( See “Use during pregnancy or lactation”)
- Children, ( See “ Pediatric use”)
- Careful administration
- Patients with severe renal disorders.
- Patients with a history of convulsive disorders. (Convulsions may possibly occur.)
- Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to quinolone antibacterial agents.
- The elderly. (see * Use in the elderly*)
- Drug interactions
- Since it has been reported that other quinolones (enoxacin, etc) used in combination with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs of phenylacetic/propionic acid derivatives, such as fenbufen, may rarely cause convulsions, this product should be administered carefully.
- Since antacids containing aluminum or magnesium and drugs containing Iron may interfere with the absorption of levofloxacin resulting in attenuation of the efficacy of levofloxacin, it is recommended to refrain from using this product with such product.
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Shock: Since shock symptoms may rarely occur, observe patients carefully. If any abnormalities are observed, discontinue the medication and take appropriate measures.
- Hypersensitivity: Anaphylactoid symptoms (erythema, chils, dyspnea) edema, Urticaria, feeling of warmth or photosensitivity may rarely occur and rash or pruritus may infrequently occur. In the event of such symptoms, discontinue the medication.
- Dermatologic: It has been reported that Levofloxacin may rarely cause Lyell Syndrome or Stevens Johnson Syndrome.
- Psychoneurologic: Convulsion, tremor or numbness may rarely occur, and insomnia, dizziness or headache may infrequently occur.
- Renal: An increase in BUN may infrequently occur. It has been reported that Levofloxacin may rarely cause acute renal failure.
- Hepatic: An increase in S-GOT, GPT, Al-Por Y-GPT or total bilirubin may infrequently occur.
- Hematologic: A decrease in leukocytes, erythrocytes, hemoglobin or hematocrit or an increase in eosinophils may infrequently occur. Observe patients carefully, and if any abnormality is observed, discontinue the medication.
- Gastrointestinal: Nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, anorexia, abdominal pain or enlarged feeling of the abdomen may infrequently occur. Since it has been reported that levofloxacin may rarely cause severe colitis, with blood in the stool, such as pseudomembranous colitis, in the event of abdominal pain or frequent diarrhea take appropriate measures, including immediate discontinuation of the medication.
- Muscular: Since rhabdomyolysis with rapid deterioration of renal function characterized by myalgia, weakness, increase in CPK or myoglobin in blood or urine may occur, patients should be cautioned.
- Others:
- Since it has been reported that other new quinolones may rarely cause hypoglycemia (especially in elderly patients with renal disorders), this product should be administered carefully.
- Malaise may rarely occur.
- Use in the elderly:
This product is mainly excreted by the kidneys. (See “Pharmacokinetics.”) Since the elderly often have a renal hypo function and are in danger of continuous high blood concentration, observe dose and interval (e.g., 100 mg. B.I.D.) - Use during pregnancy or lactation
- Since safety during pregnancy has not been established, this product should not be administered to women who are pregnant or suspected of being pregnant.
- Since Levofloxacin is excreted in breast milk, it is recommended that nursing mothers refrain from using this product. If use is necessary, breast feeding should be avoided.
- Paediatric use:
Since the product’s safety for use by children has not been established , this product should not be administered to children. - Others:
Animal studies have shown that levofloxacin can produce arthropathy in juvenile dogs, young mature dogs (13 months of age) and juvenile rats.
Storage and Handling:
Protect from light & moisture. Store at or below 25oC. Keep away from the reach of children. Once the vial is removed from the carton the infusion solution must be used within three days.
Once the vial has been opened, the infusion solution must be used within three hours.
Expiration date
Indicated on the outer package.
WARNING:
To be sold on prescription of a registered medical practitioner only.
Packaging:
Qumic 250 mg Tablets
1×10’s in Alu Alu (cold form and cold sealed) blister pack.
Qumic 500 mg Tablets
1×10’s in Alu Alu (cold form and cold sealed) blister pack.
Qumic 750 mg Tablets
1×10’s in Alu Alu (cold form and cold sealed) blister pack.
Qumic IV 500mg/100ml in glass vial.
Qumic IV 750mg/150ml in glass vial.

