

More than 200 Distributors
Around 1,000,000 Outlets
Nationwide Coverage
Micam
(Meloxicam)
Brand Name
Micam
Generic Name
(Meloxicam)
Therapeutic Segment
NSAIDs (Pain Management)

Scan QR code to open on your mobile device.
Available as
- TABLET
- MICAM 7.5MG TABLET
- MICAM 15MG TABLET
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
COMPOSITION
Each tablet contains Meloxicam BP ……..7.5mg.
Each tablet contains Meloxicam BP ……..15mg.
DESCRIPTION:
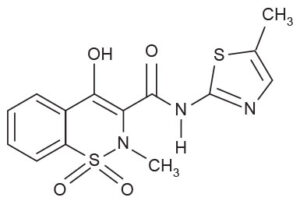
MICAM (meloxicam), an oxicam derivative, is a member of the enolic acid group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Each tablet contains meloxicam 7.5mg or 15mg for oral administration. It is chemically designated as 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(5-methyl-2-thiazolyl)-2H-1,2-benzothiazine-3-carboxamide-1, 1-dioxide.
The molecular weight is 351.4.
Its empirical formula is C14H13N304S2 and it has the following structural formula
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action: Meloxicam is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that exhibits anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic activities in animal models. The mechanism of action of meloxicam, like that of other NSAIDs, may be related to prostaglandin synthetase (cyclooxygenase) inhibition.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption:
The absolute bioavailability of meloxicam was 89% following a single oral dose of 30 mg compared with 30 mg IV bolus injection. After multiple oral doses the pharmacokinetics of meloxicam were dose-proportional over the range of 7.5 mg to 15 mg. Mean Cmax was achieved within four to five hours after a 7.5 mg meloxicam tablet was taken under fasted conditions, indicating a prolonged drug absorption. With multiple dosing, steady state concentrations were reached by day 5. A second meloxicam concentration peak occurs around 12 to 14 hours post-dose suggesting biliary recycling.
Food and Antacid Effects:
No pharmacokinetic interaction was detected with concomitant administration of antacids. MICAM tablets can be administered without regard to timing of meals and concomitant administration of antacids.
Distribution:
The mean volume of distribution (vd) of meloxicam is approximately 10 L. Meloxicam is ~99.4% bound to human plasma proteins (primarily albumin) within the therapeutic dose range. The fraction of protein binding is independent of drug concentration; over the clinically relevant concentration range, but decreases to ~99% in patients with renal disease. Meloxicam penetration into human red blood cells, after oral dosing, is less than 10%. Following a radio-labeled dose, over 90% of the radioactivity detected in the plasma was present as unchanged meloxicam. Meloxicam concentrations in synovial fluid, after a single oral dose, range from 40% to 50% of those in plasma. The free fraction in synovial fluid is 2.5 times higher than in plasma due to the lower albumin content in Synovial fluid as compared to plasma. The significance of this penetration is unknown.
Metabolism:
Meloxicam is almost completely metabolized to four pharmacologically inactive metabolites. The major metabolite, 5′-carboxy meloxicam (60% of dose), from P-450 mediated metabolism was formed by oxidation of an intermediate metabolite 5′-hydroxymethyl meloxicam which is also excreted to a lesser extent (9% of dose). In vitro studies indicate that cytochrome P-450 2C9 plays an important role in this metabolic pathway with a minor contribution of the CYP 3A4 isozyme. Patients’ peroxidase activity is probably responsible for the other two metabolites which account for 16% and 4% of the administered dose, respectively.
Excretion:
Meloxicam excretion is predominantly in the form of metabolites, and occurs to equal extents in the urine and feces. Only traces of the unchanged parent compound are excreted in the urine (0.2%) and feces (1.6%). The mean elimination half-life (t1/2) ranges from 15 hours to 20 hours. The elimination half-life is constant across dose levels indicating linear metabolism within the therapeutic dose range. Plasma clearance ranges from 7 to 9 ml/min.
Special Populations
Geriatric:
Elderly males (65 years of age) exhibited meloxicam plasma concentrations and steady state pharmacokinetics similar to young males. Elderly females (65 years of age) had a 47% higher AUC and 32% higher Cmax as compared to younger females (55 years of age) after body weight normalization. Despite the increased total concentrations in the elderly females, the adverse event profile was comparable for both elderly patient populations. A smaller free fraction was found in elderly female patients in comparison to elderly male patients.
Hepatic Insufficiency:
Following a single 15 mg dose of meloxicam there was no marked difference in plasma concentrations in subjects with mild (Child-Pugh Class I) and moderate (Child-Pugh Class II) hepatic impairment compared to healthy volunteers. Protein binding of meloxicam was not affected by hepatic insufficiency. No dose adjustment is necessary in mild to moderate hepatic insufficiency. Patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class III) have not been adequately studied.
Renal Insufficiency:
Meloxicam pharmacokinetics have been investigated in subjects with different degrees of renal insufficiency. Total drug plasma concentrations decreased with the degree of renal impairment while free AUC values were similar. Total clearance of meloxicam increased in these patients probably due to the Increase, in free fraction leading to an increased metabolic clearance. There is no need for dose adjustment in patients with mild to moderate renal failure (CrCL >15 ml/min). Patients with severe renal insufficiency have not been adequately studied. The use of MICAM in subjects with severe renal impairment is not recommended.
Hemodialysis:
Following a single dose of meloxicam, the free Cmax plasma concentrations were higher in patients with renal failure on chronic hemodialysis (1 % free fraction) in comparison to healthy volunteers (0.3% free fraction). Hemodialysis did not lower the total drug concentration in plasma; therefore, additional doses are not necessary after hemodialysis. Meloxicam is not dialyzable.
INDICATIONS:
MICAM is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug indicated for:
- symptomatic treatment of painful osteoarthritis
- symptomatic treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
- symptomatic treatment of ankylosing spondylitis
- symptomatic treatment of other painful conditions
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
MICAM (Meloxicam) is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to meloxicam. It should not be given to patients who have experienced asthma, urticaria, or allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, rarely fatal, anaphylactic-like reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients.
WARNINGS:
Gastrointestinal (GI) Effects – Risk of GI Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation: Serious gastrointestinal toxicity, such as inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach, small intestine or large intestine, can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Upper GI ulcers, gross bleeding or perforation, caused by NSAIDs, occur in approximately 1% of the patients treated for 3-6 months, and in about 2-4% of patients treated for one year. These trends continue with longer duration of use, increasing the likelihood of developing a serious GI event at some time during the course of therapy. However, even short-term therapy is not without risk.
NSAIDs should be prescribed with extreme caution in those with a prior history of ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding. Patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or gastrointestinal bleeding who use NSAIDs have a greater than 10-fold increased risk for developing a GI bleed compared to patients with neither of these risk factors. Other factors that increase the risk for GI bleeding in patients treated with NSAIDs include concomitant use of oral corticosteroids or anticoagulants, longer duration of NSAID therapy, smoking, use of alcohol, older age, and poor general health status. Most spontaneous reports of fatal GI events are in elderly or debilitated patients and therefore, special care should be taken in treating this population.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse GI event in patients treated with an NSAID, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest possible duration. Patients and physicians should remain alert for signs and symptoms of GI ulceration and bleeding during NSAID therapy and promptly initiate additional evaluation and treatment if a serious GI adverse event is suspected. This should include discontinuation of the NSAID until a serious GI adverse event is ruled out. For high-risk patients, alternate therapies that do not involve NSAIDs should be considered.
Anaphylactoid Reactions:
As with other NSAIDs, anaphylactoid reactions have occurred in patients without known prior exposure to MICAM. MICAM should not be given to patients with aspirin triad. This symptom complex typically occurs in asthmatic patients who experience rhinitis with or without nasal polyps, or who exhibit severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Emergency help should be sought in cases where an anaphylactoid reaction occurs.
Advanced Renal Disease:
In cases with advanced kidney disease, treatment with MICAM is not recommended. If NSAID therapy must be initiated, close monitoring of the patient’s kidney function is advisable.
Pregnancy:
In late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, MICAM should be avoided because it may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus.
PRECAUTIONS:
General:
MICAM cannot be expected to substitute for corticosteroids or to treat corticosteroid insufficiency. Abrupt discontinuation of corticosteroids may lead to disease exacerbation. Patients on prolonged corticosteroid therapy should have their therapy tapered slowly if a decision is made to discontinue corticosteroids.
The pharmacological activity of MICAM in reducing inflammation and fever may diminish the utility of these diagnostic signs in detecting complications of presumed noninfectious, painful conditions.
Hepatic Effects:
Borderline elevations of one or more liver tests may occur in up to 15% of patients taking NSAIDs, including Meloxicam. These laboratory abnormalities may progress, may remain unchanged, or may be transient with continuing therapy. Notable elevations of ALT or AST (approximately three or more times the upper limit of normal) have been reported in approximately 1% of patients in clinical trials with NSAIDs. In addition, rare cases of severe hepatic reactions, including jaundice and fatal fulminant hepatitis, liver necrosis and hepatic failure, some of them with fatal outcomes, have been reported.
Patients with signs and/or symptoms suggesting liver dysfunction, or in whom an abnormal liver test has occurred, should be evaluated for evidence of the development of a more severe hepatic reaction while on therapy with MICAM. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.), MICAM should be discontinued.
Renal Effect:
Caution should be used when initiating treatment with MICAM in patients with considerable dehydration. It is advisable to rehydrate patients first and then start therapy with MICAM. Caution is also recommended in patients with pre-existing kidney disease.
The extent to which metabolites may accumulate in patients with renal failure has not been studied with Meloxicam. Because some Meloxicam metabolites are excreted by the kidney, patients with significantly impaired renal function should be more closely monitored.
Hematological Effects:
Anemia is sometimes seen in patients receiving NSAIDs, including Meloxicam. This may be due to fluid retention, GI blood loss, or an incompletely described effect upon erythropoiesis. Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs, including Meloxicam, should have their hemoglobin or hematocrit checked if they exhibit any signs or symptoms of anemia.
Drugs which inhibit the biosynthesis of prostaglandins may interfere to some extent with platelet function and vascular responses to bleeding. NSAIDs inhibit platelet aggregation and have been shown to prolong bleeding time in some patients. Unlike aspirin their effect on platelet function is quantitatively less, or of shorter duration, and reversible. Patients receiving Meloxicam who may be adversely affected by alterations in platelet function, such as those with coagulation disorders or patient receiving anticoagulants, should be carefully monitored.
Pre-existing Asthma:
Patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma. The use of aspirin in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma has been associated with severe bronchospasm which can be fatal. Since cross reactivity, including bronchospasm, between aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs has been reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, MICAM should not be administered to patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity and should be used with caution in patients with pre-existing asthma.
Laboratory Tests: Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs should have their CBC and a chemistry profile checked periodically. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver or renal disease develop, systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash etc.) or if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, MICAM (Meloxicam) should be discontinued.
Drug Interactions:
ACE Inhibitors: Reports suggest that NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE Inhibitors. This Interaction should be given consideration in patients taking NSAIDs concomitantly with ACE inhibitors.
Aspirin:
When meloxicam administered with aspirin (1000mg TID) to healthy volunteers, it tended to increase the AUC (10%) and Cmax (24%) of meloxicam. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known: however, as with other NSAIDs, concomitant administration of meloxicam and aspirin is not generally recommended because of the potential for increased adverse effects. Concomitant administration of low-dose aspirin with MICAM may result in an increased rate of GI ulceration or other complications, compared to use of MICAM alone. MICAM is not a substitute for aspirin for cardiovascular prophylaxis.
Cimetidine:
Concomitant administration of 200mg cimetidine QID did not alter the single-dose pharmacokinetics of 30mg meloxicam.
Digoxin:
Meloxicam 15mg once daily for 7 days did not alter the plasma concentration profile of digoxin after β-acetyldigoxin administration for 7 days at clinical doses. In vitro testing found no protein binding drug interaction between digoxin and meloxicam.
Furosemide:
Clinical studies, as well as post-marketing observations, have shown that NSAIDs can reduce the natriuretic effect of furosemide and thiazide in some patients. This response has been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. Studies with furosemide agents and meloxicam have not demonstrated a reduction in natriuretic effect. Furosemide single and multiple dose pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetics are not affected by multiple doses of meloxicam. Nevertheless, during concomitant therapy with furosemide and MICAM, patients should be observed closely for signs of renal failure, as well as to assure diuretic efficacy.
Lithium:
In a study conducted in healthy subjects, mean pre-dose Lithium concentration and AUC were increased by 21% in subjects receiving lithium doses ranging from 804 to 1072mg BID with meloxicam 15mg OD as compared to subjects receiving lithium alone. These effects have been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis by Meloxicam.
Patients on lithium treatment should be closely monitored for sign of lithium toxicity when MICAM is introduced, adjusted, or withdrawn.
Methotrexate:
A study in 13 rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients evaluated the effects of multiple doses of meloxicam on the pharmacokinetics of methotrexate taken once weekly. Meloxicam did not have a significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of single doses of methotrexate. In vitro, methotrexate did not displace meloxicam from its human serum binding sites.
Warfarin:
The effects of warfarin and NSAIDs on GI bleeding are synergistic, such that users of both drugs together have a risk of serious GI bleeding higher than users of either drug alone. Anticoagulant activity should be monitored, particularly in the first few days after initiating or changing MICAM therapy in patients receiving warfarin or similar agents, since these patients are at an increased risk of bleeding. The effect of meloxicam on the anticoagulant effect of warfarin was studied in a group of healthy subjects receiving daily doses of warfarin that produced an INR (International Normalized Ratio) between 1.2 and 1.8. In these subjects, meloxicam did not alter warfarin pharmacokinetics and the average anticoagulant effect
of warfarin as determined by prothrombin time. However, one subject showed an increase in INR from 1.5 to 2.1. Caution should be used when administering MICAM with warfarin since patients on warfarin may experience changes in INR and an increased risk of bleeding complications when a new medication is introduced.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, impairment of Fertility
No carcinogenic effect of meloxicam was observed in rats given oral doses up to 0.8mg/kg/day (approximately 0.4-fold the human dose at 15mg/day for a 50kg adult based on body surface area conversion) for 104 weeks or in mice given oral doses up to 8.0 mg/kg/day (approximately 2.2-fold the human dose, as noted above) for 99 weeks. Meloxicam was not mutagenic in an Ames assay, or clastogenic in a chromosome aberration assay with human lymphocytes and an in vivo micronucleus test in mouse bone marrow. Meloxicam did not impair male and female fertility in rats at oral doses up to 9 and 5 mg/kg/day, respectively (4.9-fold and 2.5-fold the human dose, as noted above). However, an increased incidence of embryolethality at oral doses 1mg/kg/day (0.5-fold the human dose, as noted above) was observed in rats when dams were given meloxicam 2 weeks prior to mating and during early embryonic development.
PREGNANCY:
Teratogenic Effects:
Pregnancy category C:
Meloxicam caused an increased incidence of septal defect of the heart, a rare event, at an oral dose of 60mg/kg/day (64.5-fold the human dose at 15mg/day for a 50kg adult based on body surface area conversion) and embryolethality at oral doses 5mg/kg/day (5.4-fold the human dose, as noted above) when rabbits were treated throughout organogenesis. Meloxicam was not teratogenic in rats up to an oral dose of 4mg/kg/day (approximately 2.2-fold the human dose as noted above) throughout organogenesis. An increased incidence of stillbirths was observed when rats were given oral doses 1mg/kg/day throughout organogenesis. Meloxicam Crosses the placental barrier. There are no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women. MICAM should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Non-teratogenic Effects:
Meloxicam caused a reduction in birth index, live births, and neonatal survival at oral doses 0.125mg/kg/day (approximately 0.07-fold the human dose at 15mg/day for a 50kg adult based on body surface area conversion) when rats were treated during the late gestation and lactation period. No studies have been conducted to evaluate the effect of meloxicam on the closure of the ductus arteriosus in humans; use of meloxicam during the third trimester of pregnancy should be avoided.
Labor and Delivery:
Studies in rats with meloxicam, as with other drugs Known to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, showed an increased incidence of stillbirths, prolonged delivery, and delayed parturition at oral dosages 1mg/kg/day (approximately 0.5-fold the human dose at 15mg/day for a 50kg adult based on body surface area conversion), and decreased pup survival at an oral dose of 4mg/kg/day (approximately 2.1-fold the human dose, as noted above) throughout organogenesis. Similar finding were observed in rats receiving oral dosages 0.125 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.07-fold the human dose, as noted above) during late gestation and the lactation period.
Nursing Mothers:
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk however, meloxicam was excreted in the milk of lactating rats at concentrations higher than those in plasma. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from MICAM,
a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Geriatric Use:
As with any NSAID, caution should be exercised in treating the elderly (65 years and older).
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
Gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events were the most frequently reported adverse events in all treatment groups across Meloxicam trials. The adverse events reported include abdominal pain, diarrhoea, flatulence, nausea, oedema, dizziness, headache, skin rash, insomnia, flu like syndrome, etc. As with other NSAIDs, higher doses of Meloxicam (e.g., chronic daily 30mg dose) were associated with an increased risk of serious GI events, therefore the daily dose of MICAM should not exceed 15mg.
SIDE EFFECTS:
The following is a list of adverse drug reactions occurring in < 2% of patients receiving Meloxicam in clinical trials involving approximately 16,200 patients. Adverse reactions reported only in worldwide post-marketing experience.
Body as a Whole:
Allergic reaction, anaphylactoid reactions including shock, face edema, fatigue, fever, hot flushes, malaise, syncope, weight decrease, weight increase.
Cardiovascular:
Angina pectoris, cardiac failure, hypertension, hypotension, myocardial infarction, vasculitis.
Central and Peripheral Nervous System:
Convulsions, paresthesia, tremor, vertigo.
Gastrointestinal:
Colitis, dry mouth, duodenal ulcer, eructation, esophagitis, gastric ulcer, gastritis, gastroesophageal reflux, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, hematemesis, hemorrhagic duodenal ulcer, hemorrhagic gastric ulcer, intestinal perforation, melena, pancreatitis, perforated duodenal ulcer, perforated gastric ulcer, stomatitis ulcerative.
Heart Rate and Rhythm:
Arrhythmia, palpitation, tachycardia.
Hematologic:
Agranulocytosis, leukopenia, purpura, thrombocytopenia.
Liver and Biliary System:
ALT increased, AST increased, bilirubinemia, GGT increased, hepatitis, jaundice, liver failure.
Metabolic and Nutritional:
Dehydration.
Psychiatric:
Abnormal dreaming, alterations in mood (such as mood elevation), anxiety, appetite increased, confusion, depression, nervousness, somnolence.
Respiratory:
Asthma, bronchospasm, dyspnea.
Skin and Appendages:
Alopecia, angioedema, bullous eruption, erythema multiforme, photosensitivity reaction, pruritus, exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, sweating increased, toxic epidermal necrolysis, urticaria.
Special Senses:
Abnormal vision, conjunctivitis, taste perversion, tinnitus.
Urinary System:
Acute urinary retention, albuminuria, BUN increased, creatinine increased, hematuria, interstitial nephritis, renal failure.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
The lowest dose of MICAM should be sought for each patient.
For the treatment of osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis and Ankylosing spondylitis the recommended starting and maintenance dose of MICAM is 7.5mg once daily. Some patients may receive additional benefit by increasing the dose to 15mg once daily.
The maximum recommended daily dose of MICAM is 15mg.
MICAM may be taken without regard to timing of meals.
OVERDOSAGE:
There is limited experience with meloxicam overdose. Four cases have taken 6 to 11 times the highest recommended dose; all recovered. Cholestyramine is known to accelerate the clearance of meloxicam. Symptoms following acute NSAID overdose are usually limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain, which are generally reversible with supportive care:
Gastrointestinal bleeding can occur. Severe poisoning may result in hypertension, acute renal failure, hepatic dysfunction, respiratory depression, coma, convulsions, cardiovascular collapse, and cardiac arrest. Anaphylactoid reactions have been reported with therapeutic ingestion of NSAIDs, and may occur following an overdose.
Patients should be managed with symptomatic and supportive care following an NSAID overdose. In cases of acute overdose, gastric lavage followed by activated charcoal is recommended. Gastric lavage performed more than one hour after overdose has little benefit in the treatment of overdose. Administration of activated charcoal is recommended for patients who present 1-2 hours after overdose. For substantial overdose or severely symptomatic patients, activated charcoal may be administered repeatedly. Accelerated removal of meloxicam by 4gm oral doses of cholestyramine given three times a day was demonstrated in a clinical trial. Administration of cholestyramine may be useful following an overdose.
Forced diuresis, alkalinization of urine, hemodialysis, or hemoperfusion may not be useful due to high protein binding.
DIRECTION FOR USE:
Protect from light and moisture, Store below 25°C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
WARNING:
To be sold on prescription of a registered medical practitioner only.
PRESENTATION:
MICAM 7.5mg pack of 10’s Tablets
MICAM 15mg pack of 10’s Tablets

